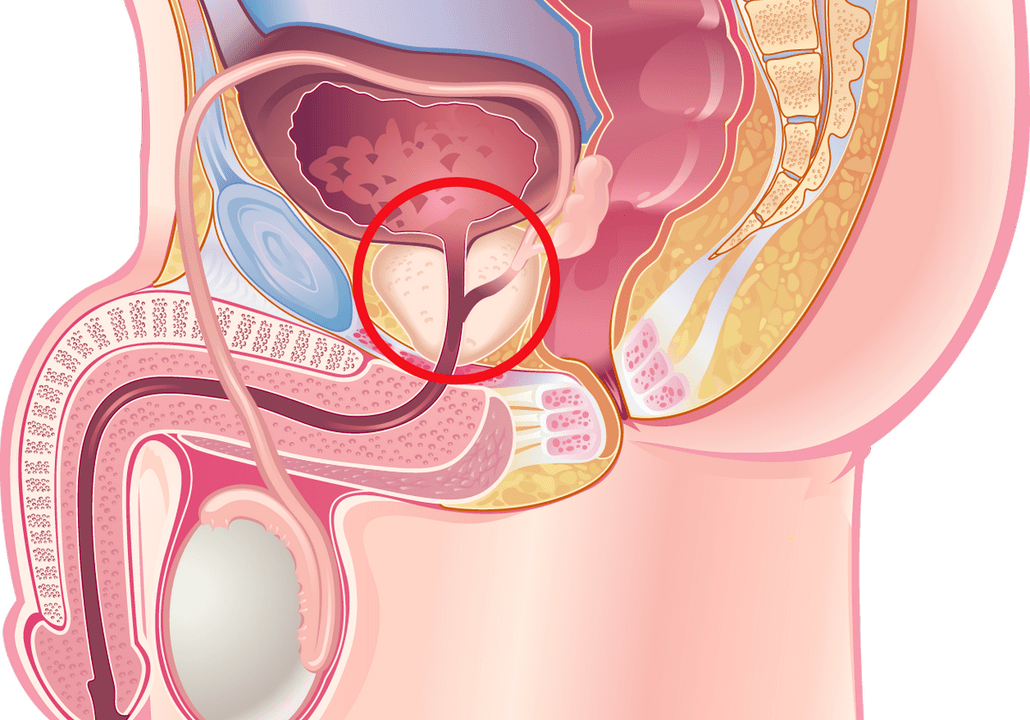
Prostatitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory disease of the prostate. The acute form is characterized by pronounced symptoms. In the absence of adequate treatment, it becomes chronic. This variant of prostatitis is less treatable, can lead to malignant degeneration of glandular tissues.
At the medical center, every man can undergo a comprehensive examination to identify any form of prostatitis. The center is equipped with modern high-precision equipment. In the laboratory, you can take all the tests prescribed by the doctor. Experienced urologists of the highest qualification category will draw up an individual treatment plan taking into account the characteristics of each clinical case.
About the disease
Prostatitis is a common problem that affects about 40% of men over the age of 40. It does not directly threaten a person's life, however, by reducing efficiency, affecting the patient's neuropsychic sphere, limiting freedom, prostatitis significantly deteriorates the quality of life.
Inflammation of the prostate can occur as an independent pathology or be associated with an adenoma or cancer of this organ.
Kinds
In 1996, a classification was developed, according to which there are 4 categories of prostatitis in men:
- Acute prostatitis.
- Chronic prostatitis of a bacterial nature.
- Chronic inflammation of the prostate of a non-bacterial nature.
- IIIA. With the presence of signs of inflammation (leukocytes and all microorganisms are found in the secretion of the prostate).
- IIIB. Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis without an inflammatory component (there are no leukocytes and microorganisms in the secretion of the prostate).
- Asymptomatic chronic prostatitis (a person does not complain, but leukocytes are found in the secretion of the prostate).
Symptoms of prostatitis
Depending on the form of the disease, prostatitis can come on suddenly, manifest itself in vivid clinical symptoms, or proceed with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
Common signs of prostatitis in men:
- varying intensity of pain in the perineum, radiating to the groin and sacrum;
- lower back pain;
- urination disorders (pain at the start of the act and throughout its duration, intermittent urine stream, possibly drop by drop urination, frequent urge);
- decreased potency and libido;
- painful ejaculation;
- pain after intercourse;
- erectile dysfunction;
- intoxication syndrome - weakness, fatigue, fever, headache, sometimes nausea, vomiting.
Not all of these symptoms will necessarily be determined by the same man - perhaps a different combination of them. With an exacerbation of chronic prostatitis, they are usually less pronounced than in the acute form of the disease, and in remission they are practically not determined. Disorders of sexual function often occur in men who have suffered from chronic prostatitis for more than 5 years.
If prostatitis is neglected, the risk of developing prostate adenoma and cancer, infertility, difficult to treat impotence increases. Having identified the first symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to contact a urologist as soon as possible. This will allow a comprehensive treatment that stops the pathological process.
Causes of prostatitis
Assign infectious and non-infectious causes of prostatitis.
Acute infectious prostatitis is caused by bacteria, more often - Enterobacter, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Proteus and sexually transmitted infections, less often - Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The spectrum of microorganisms that can cause an exacerbation of chronic prostatitis is much wider and can include both opportunistic and atypical (candida) infections.
The microorganism enters the prostate through the urethra, bladder, less often with blood or lymph flow from distant foci of infection.
Factors that increase the risk of developing the disease:
- STDs;
- remotely localized chronic infectious diseases (caries, sinusitis, lung abscess);
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiencies;
- manipulations and operations on the pelvic organs;
- prostate biopsy;
- sedentary lifestyle, accompanied by stagnation of blood in the pelvic region;
- promiscuous sex life;
- same-sex contact.
The causes of non-infectious forms of prostatitis are not fully understood. It is believed to be associated with the stagnation of the secret in the prostate due to a violation of the venous outflow from the pelvic organs. The vessels of the prostate overflow with blood, swell, all functions of the gland are disturbed, signs of inflammation appear. The risk factors for the development of this form of prostatitis are:
- autoimmune processes (attack by antibodies from the body of prostate cells);
- prolonged absence of sexual activity;
- prolonged or interrupted sexual intercourse;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- unfavorable working conditions (vibration impact);
- chronic poisoning with certain chemicals;
- spinal cord injury;
- hemorrhoids;
- constipation;
- androgen deficiency in the body of a man.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
Prostatitis is diagnosed on the basis of patient complaints, examination data, anamnesis and the results of additional studies. In order to detect the disease, apply:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- study of prostatic secretion;
- analysis of biological fluids for urogenital infections;
- transurethral ultrasound of the prostate (TRUS);
- prostate specific antigen test;
- determination of testosterone levels;
- Urine analysis.
Treatment of prostatitis
When the diagnosis is established, the man is prescribed a complex drug treatment. It includes antibacterial drugs, enzymes, herbal remedies, immunomodulators. If the patient follows all the recommendations of the urologist, the treatment of acute prostatitis on an outpatient basis leads to complete recovery. Conversely, a violation of the treatment regimen leads to the emergence of highly resistant forms of microorganisms that cannot be destroyed by traditional antibiotics. As a result, inflammatory and dystrophic processes are aggravated, the disease becomes chronic.
Chronic prostatitis is difficult to cure. This requires an integrated approach with the appointment of a long drug treatment and special treatment procedures. The clinic's urology specialists draw up an individual treatment plan for the patient, which includes:
- antibiotic therapy for up to a month;
- angioprotectors;
- enzyme treatment;
- non-steroids which stop the inflammatory reaction;
- immunomodulatory treatment (selected by an immunologist);
- prostate massage;
- instillations into the urethra, if the inflammatory process is localized in the urethra;
- physiotherapy.
The patient may receive treatment in the hospital or outpatient clinic. In the first case, the chances of a positive result increase, since the man strictly observes the diet, adheres to all the doctor's prescriptions and is under close medical supervision.
In case of complications of prostatitis (suppuration of seminal vesicles, prostate abscess), surgical treatment can be shown to a man.
Physiotherapy treatment
Unique modern devices for local impact on the prostate are installed in the specialized center. Physiotherapy increases the effectiveness of complex treatments, reduces the resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics and eliminates congestion in the body. For the treatment of prostatitis, experienced doctors use:
- "A device for a complex effect on the prostate and pelvic muscles, accelerated treatment of prostatitis and relief of its symptoms. Therapeutic effect is due to electrical stimulation, laser and magnetic radiation. It improves drainageof the gland, activates blood circulation in the pelvis, eliminates the inflammatory process and improves the penetration of drugs into the tissues of the organ.
- Vacuum massage device, restores the vascular trophism of the cavernous bodies of the penis and improves blood circulation in the pelvic organs. It is used to treat prostatitis associated with obvious erectile dysfunction, as well as in the complex treatment of impotence. Eliminates the causes of congestion, tk. tones the blood vessels.
- Device for local heating of the prostate. Heating tissues up to 39-42°C inhibits the reproduction of microorganisms, triggers metabolic processes in the prostate and improves its blood supply. It is used to treat various forms of prostatitis.
A modern clinic helps men cope with chronic prostatitis in the shortest possible time. Experienced specialists will definitely establish the causes of the pathology and choose an effective treatment. By signing up for physiotherapy, you will speed up recovery, quickly get rid of pain and discomfort.
Prevention
Specific prevention of prostatitis in men has not been developed. Non-specific measures include patient compliance with a number of recommendations:
- drink enough fluids;
- do not tolerate, if you want to go to the toilet, empty your bladder regularly;
- lead an active sex life;
- avoid hypothermia;
- avoid hypodynamia;
- observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- timely treat urogenital infections and any other infectious diseases of the body;
- reduce the amount of spicy foods, caffeine and alcoholic beverages in the diet, as they have an irritating effect on the urinary tract.
Rehabilitation
In a short time, an active lifestyle, compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician for maintenance therapy and proper nutrition will help a man recover from acute or exacerbated prostatitis in a short time.
To avoid stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, a person needs to move more, and if his work involves physical inactivity (for example, a long stay behind the wheel) - as far as possible, get out of the car and move, go toyou at the gym.
Properly organized nutrition will speed up recovery and reduce the risk of exacerbation of the disease. It is important to consume a large amount of plant foods - vegetables, oils, as well as dairy products and fiber.
Questions and answers
Which doctor should I contact if I suspect prostatitis?
A urologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of prostatitis.
Is it possible to fully recover from prostatitis?
Depending on the form of the disease occurring in a particular patient. Acute prostatitis, if a person consults a doctor in a timely manner and follows all treatment recommendations, can soon pass without a trace. Chronic prostatitis, alas, is not curable. However, the correct treatment tactics and a responsible attitude of a man to the problem will significantly increase the chances of achieving long-term stable remission.
Chronic prostatitis can be defeated! To get quality care, don't delay treatment.